Abnormally slow heart rhythm
An Introduction to Arrhythmias
An arrhythmia is an abnormal rhythm of the heart. Physicians prescribe the iRhythm monitoring service, which includes Zio® ECG monitors, to detect these abnormalities.
Overview of arrhythmias
What is an arrhythmia?1
An arrhythmia is an abnormal rhythm of the heart. Arrhythmias are labeled by the location in the heart where they originate. Rhythms that start in the lower chambers, or ventricles, are called ventricular arrhythmias, while those that start in the upper chambers, or atria, are called supraventricular arrhythmias.
What are common symptoms of arrhythmia?2
Some patients may feel symptoms, while others may not. Common symptoms include:
- Heart palpitations
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Syncope/fainting
- Fatigue/tiredness
- Anxiety
Common types of arrhythmias
Bradycardia
Common types3:
- Sinus bradycardia: The upper chambers produce a slower than normal heartbeat, also referred to as sinus node dysfunction or sick sinus syndrome
- Heart block: Conduction slows in the bottom chambers. There are several types of heart block. Treatment will be dependent on the type.
- 1st degree: Signal is slowed or delayed from the atrium to the ventricle
- Wenckebach: A type of 2nd-degree heart block, also referred to by clinicians as Mobitz I
- Mobitz II: A type of 2nd-degree heart block
- Complete heart block (CHB): Also referred to by clinicians as 3rd-degree heart block
Tachycardia
Abnormally fast heart rhythm
Common types3:
- Premature beat: Extra, early heartbeats, often referred to as a PAC/SVE or PVC/VE
- Atrial fibrillation (AFib): The heart's upper chambers (atria) quiver or fibrillate, leading to a fast, irregular heartbeat
- Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT): The upper chambers beat too quickly in an abnormal conduction pattern
- Ventricular tachycardia (VT): The lower chambers beat too rapidly
Detecting irregular heart rhythms
Fortunately, there are treatments available for arrhythmias. However, before you can begin treatment, the condition must be diagnosed. There are a variety of tests that provide data to help your doctor prescribe the most effective form of treatment.
What is an ECG?4
An electrocardiogram — abbreviated as ECG or EKG — is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heartbeat. With each beat, an electrical impulse (or “wave”) travels through the heart. This wave causes the muscle to squeeze and pump blood from the heart. A normal heartbeat on ECG will show the timing of the top and lower chambers.
What is ambulatory cardiac monitoring?5
An ambulatory ECG records the electrical activity of your heart while you are doing your normal everyday activities. “Ambulatory” means that you are able to stand and walk, and are not stationary or motionless. Many heart problems are only detectable during activity such as standing or walking and will not appear in a brief test in your doctor’s office.
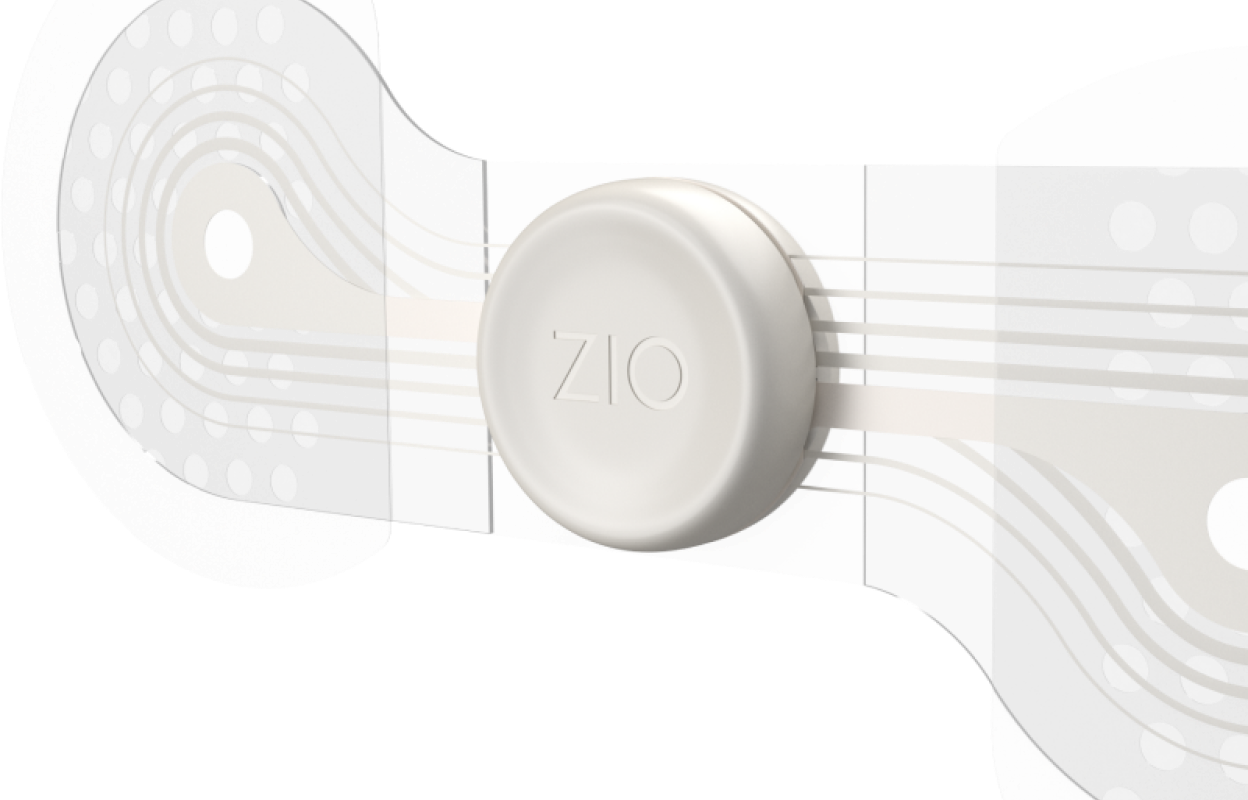

The iRhythm monitoring service, utilizing Zio ECG monitors, has been prescribed for millions of patients6 to aid in detecting arrhythmias. Using the collected monitoring data, your doctor can recommend the most appropriate treatment.7
For specific medical questions, contact your physician. For more information, visit Upbeat or American Heart Association.
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Types of arrhythmias. National Institutes of Health. Last updated March 24, 2022. Accessed December 17, 2024. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/arrhythmias/types
- Symptoms listed are from Zio monitor Indications for Use.
- Heart Rhythm Society. Electrical. UpBeat.org. Last updated February 24, 2021. Accessed December 17, 2024. https://upbeat.org/heart-rhythm-disorders/electrical
- American Heart Association. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). Last reviewed December 7, 2022. Accessed December 17, 2024. https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/heart-attack/diagnosing-a-heart-attack/electrocardiogram-ecg-or-ekg
- Fabian et al. Ambulatory ECG Monitoring. In: StatPearls [Internet]. 2024 Jan. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing. Updated November 2, 2023. Accessed December 20, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK597374/
- Data on file. iRhythm Technologies, 2023.
- Data on file. iRhythm Technologies, 2022-2023.
WEB0020.01